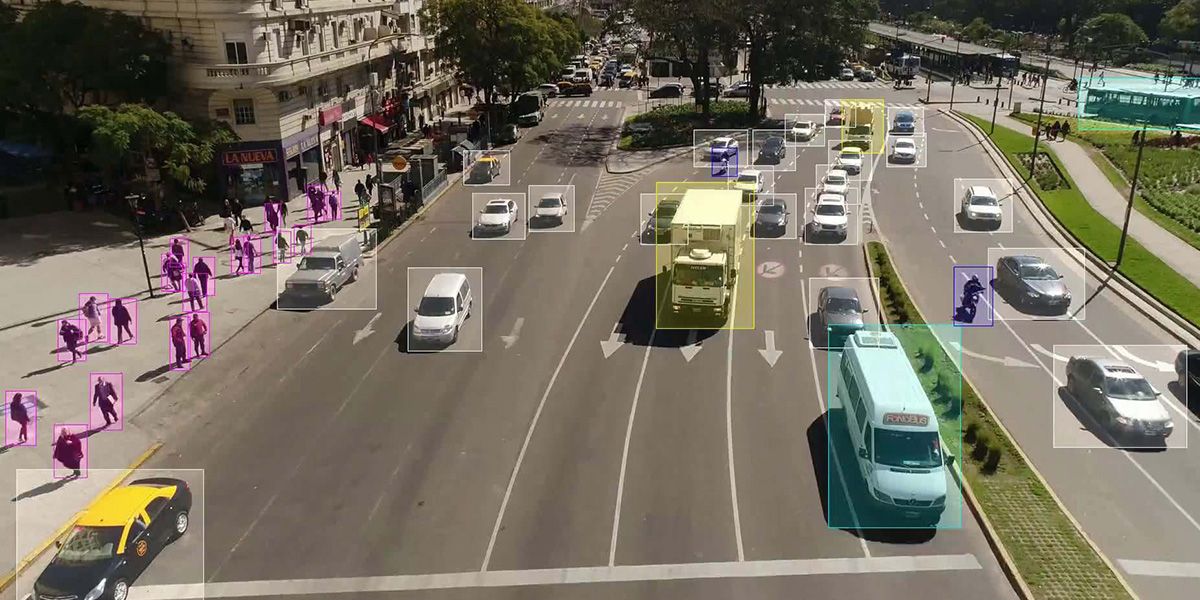
How AI Sees the World Like a Human
One of the most groundbreaking applications of artificial intelligence (AI) today is in the development of autonomous vehicles. At the heart of a self-driving car’s decision-making system lies computer vision a branch of AI that allows machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world. Much like human drivers use their eyes to perceive the road, computer vision enables autonomous vehicles to “see” and react to their surroundings in real time.
What is Computer Vision?
Computer vision is the field of AI that trains machines to recognize patterns, objects, and context in images or video. It combines deep learning, neural networks, and vast datasets to teach computers how to extract meaning from visual input. For autonomous vehicles, this means being able to identify other vehicles, pedestrians, road signs, traffic lights, lane markings, and unexpected obstacles and to do so accurately, quickly, and under different environmental conditions.
How Self-Driving Cars “See”
Autonomous vehicles rely on a fusion of sensors, including cameras, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, and ultrasonic sensors. Among these, cameras are the primary source for computer vision. AI models process the video feeds from multiple cameras placed around the vehicle, analyzing each frame to detect and classify objects, estimate distances, and track motion.
Unlike humans, AI can process visual data from multiple directions simultaneously. It can detect subtle patterns, such as the difference between a shadow and a solid object, or predict the intention of a pedestrian about to cross the street. Using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and real-time object detection algorithms like YOLO or Faster R-CNN, the system identifies what’s around the car and where it is located in space.
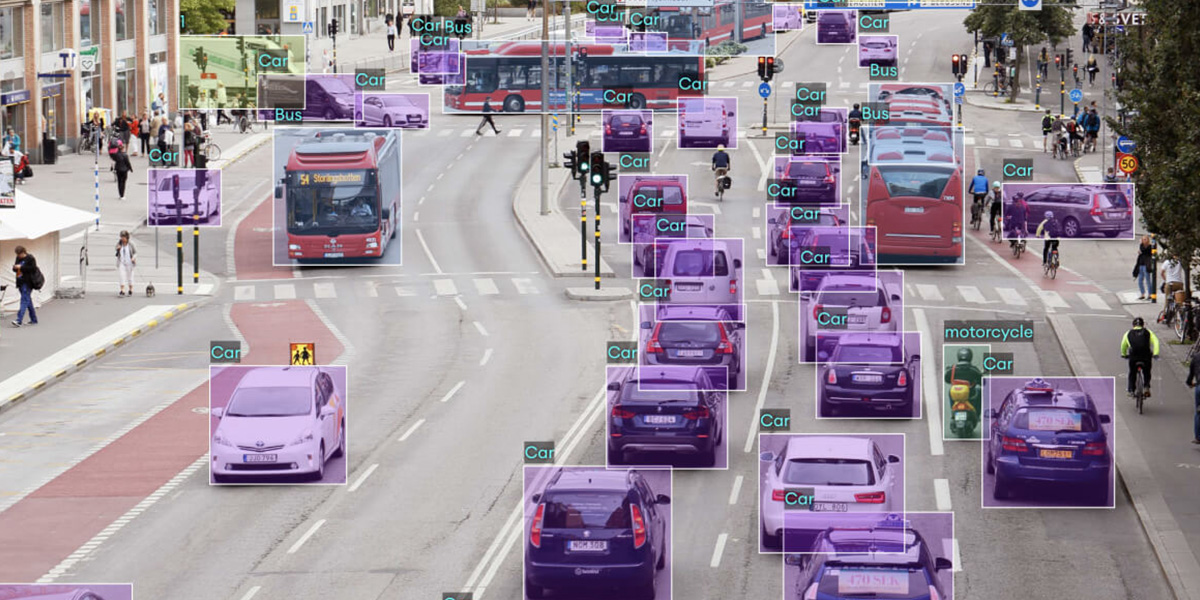

Mimicking Human Perception
While human drivers rely on intuition, experience, and a wide field of vision, computer vision uses mathematical models trained on millions of images and driving scenarios. In many cases, AI systems can outperform humans in reaction time, night vision, or multitasking. However, replicating human level perception especially in ambiguous or unpredictable situations remains a major challenge.
To overcome this, self-driving systems often use sensor fusion, combining data from vision, radar, and LiDAR to build a comprehensive and accurate 3D map of the environment. This allows the vehicle to make better decisions, even in complex or poor visibility conditions.
Challenges in AI Vision
Despite the progress, computer vision in autonomous vehicles still faces significant challenges. These include:
- Recognizing partially obstructed objects
- Handling extreme weather conditions (rain, snow, fog)
- Adapting to new road types or construction zones
- Real-time processing at high speeds with low latency
Developers continuously train and refine AI models using synthetic data, simulation environments, and real-world testing to improve robustness and reliability.
The Road Ahead
As computer vision technologies evolve, autonomous vehicles are getting closer to matching and eventually surpassing human driving ability. With safer perception systems, cars will be able to drive not just with sight, but with intelligence, anticipation, and adaptability.
Conclusion
Computer vision is the eye of the self-driving car. By enabling machines to understand the road like a human, AI is laying the foundation for a future where transportation is safer, smarter, and truly autonomous.

